Welcome to FMEP’s Weekly Settlement Report, covering everything you need to know about Israeli settlement activity this week.
To subscribe to this report, please click here.
October 22, 2021
- Israel to Advance Plans for Nearly 3,000 Settlement Units & 1,300 Palestinian Homes in Area C
- Israeli Supreme Court to Hold Hearing on Batan al-Hawa, Silwan Dispossession Cases Next Week; AG Declines Intervention
- Israel Begins Construction on New Settlement in Downtown Hebron
- Israel Advances “Silicon Wadi” Project in East Jerusalem
- Recap: Israel Advances Settlement Plans Across Greater Jerusalem Area
- Recap: Court Pushes for Palestinians to “Compromise” with Settlers in Sheikh Jarrah
- New Report: State-Backed Settler “Tourism” Projects in East Jerusalem
- Bonus Reads
Israel to Advance Plans for Nearly 3,000 Settlement Units & 1,300 Palestinian Homes in Area C
The Israeli Civil Administration’s High Planning Council will convene next week — for the first time since Bennett and Biden took over leadership in Israel and the U.S., respectively — to advance the construction of 2,862 new settlement units (of which 1,231 will be eligible to receive final approval). These plans include the retroactive legalization of two unauthorized outposts (Mitzpe Danny and Haroeh Haivri), which should be properly understood as the creation of two new settlements.
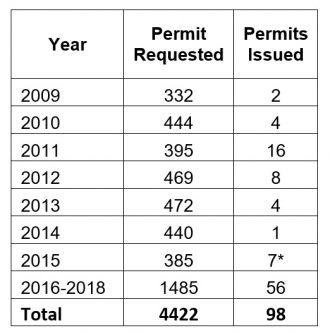
In addition, reports suggest that Israel will also advance plans for 1,303 Palestinian homes in Area C – about half of which, importantly, are already built. A majority of these units have been awaiting Israeli approval for many, many years. If approved, the permits under consideration next week for Palestinians will be the first of any significant quantity issued by Israel since, at least, 2009 (data from before this period has not been released by the Israeli government). Between 2009 and 2018, Israel issued a total of 98 building permits to Palestinians according to data released by the Israeli government in response to a freedom of information request submitted by Bimkom.
As a reminder, Area C is the 60% of the West Bank over which Israel enjoys absolute authority. For years Israel has systematically denied Palestinians the right to build on land in Area C that even Israel recognizes is privately owned by them, At the same time, it has continuously promoted the expansion of settlements and unauthorized outposts, while systematically demolishing Palestinian private construction. In terms of numbers: between 2016 to 2018, Israel issued only 21 building permits to Palestinians in Area C, while issuing 2,147 demolition orders against Palestinians during.
Commenting on the Planning Council agenda’s Peace Now observed:
“The approval of a handful of plans for the Palestinians is only a fig leaf intended to try to reduce criticism of the government. For years, Israel has pursued a policy of blatant discrimination that does not allow almost any construction for Palestinians in Area C, while in the settlements it encourages and promotes the construction of thousands of housing units each year for Israelis. The approval of a few hundred housing units for Palestinians can not cover up discrimination and does not change the fact that Israel maintains an illegal regime of occupation and discrimination in the territories.”
It is worth noting that many of the settlement units and Palestinian permits on next week’s agenda were expected to have been advanced earlier this year, in August 2021, but the High Planning Council never convened to do so.
Below are lists of settlement plans expected to be given final approval and plans expected to be advanced next week (italicized plans represent those which appear to have been added to the slate of plans that were expected to be advanced in August 2021).
Settlement plans expected to be granted final approval include:
- 629 units, including the retroactive legalization of 61 units, in the Eli settlement – located south of Nablus and southeast of the Ariel settlement in the central West Bank. Though the Eli settlement previously received Israeli government approval, a “Master Plan” – which officially zones land for distinct purposes (residential, commercial, public) – has never been issued for Eli, meaning all construction there is illegal under Israeli law;
- 286 units in the Har Bracha settlement, located south of Nablus. If implemented, these new units will double the size of Har Bracha;
- 224 units in the Talmon settlement, located west of Ramallah;
- 146 units in the Kfar Etzion settlement, located between Bethlehem and Hebron and on the Israeli side of the planned route of the barrier (which is not yet built in this area);
- 110 units in the Alon Shvut settlement, located just north of the Kfar Etzion settlement and between Bethlehem and Hebron;
- 82 units in the Karnei Shomron settlement, located in the northern West Bank, east of the Palestinian village of Qalqilya. Israel has openly declared its intention to continue expanding settlements in this area with the stated goal of bringing 1 million settlers to live in the area.;
- 52 units in the Beit El settlement, located in the heart of the northern West Bank [as a reminder, former US Ambassador to Israel David Friedman has deep ties to the Beit El settlement]; Construction on 350 new units in Beit El began earlier this year;
- 42 units in the Givat Zeev settlement, located south of Ramallah in an area that is on the Israeli side of the barrier;
- 24 units in the Haroeh Haivri outpost, a plan that will effectively grant retroactive legalization to this outpost. The Haroeh Haivri outpost is located just east of Jerusalem, within eyesight of the Khan al-Ahmar community, which Israel is threatening to demolish (forcibly relocating the Palestinian bedouin community that has lived there since the 1950s) — ostensibly because the structures in Khan al Ahmar were built without necessary Israeli approvals. The Haroah Haivri outpost was also built without the necessary Israeli approvals, but instead of demolishing the construction, Israel is moving to retroactively legalize it — demonstrating once again that, when it comes to administering the occupation, Israel prefers “rule by law” – where law is turned into a tool to elevate the rights/interests of one party over another, over the democratic rule of law.;
- 14 units in the Ma’aleh Mikhmash settlement, a plan that will effectively grant retroactive legalization to one of Ma’aleh Mikhmash’s outposts – – Mitzpe Danny;
- 10 units in the Barkan settlement, located about half way between the Ariel settlement and the cluster of settlements slated to be united into a “super settlement” area (Oranit, Elkana, Shiva Tikva, and others);
- 5 units in the Shima’a settlement, located in the southern tip of the West Bank;
- 7 units in the Peduel settlement, located in the northern West Bank and part of a string of settlements and unauthorized outposts – most notably Ariel – extending from the Green Line into the very heart of the West Bank and on towards the Jordan Valley.
Settlement plans expected to be approved for deposit (an earlier stage in the planning process) include:
- 399 units in the Revava settlement, located just east of the Barkan settlement and west of the Ariel settlement, in a string of settlements and unauthorized outposts – most notably Ariel – extending from the Green Line into the very heart of the West Bank and on towards the Jordan Valley.
- 380 units in the Kedumim settlement, located just east of Nablus. Israeli MK Bezalel Smotrich lives in the Kedumim settlement on a section of land in the settlement that has been found to be privately owned by Palestinians.;
- 100 units in the Elon Moreh settlement, located east of Nablus (for background on the significance of the Elon Moreh settlement, please see here);
- 100 units in the Sansana settlement, located on the southern tip of the West Bank on the Israeli side of the separation barrier;
- 73 units in the Givat Zeev settlement, which is also expected to receive final approval for 42 units. Givat Zeev is located south of Ramallah in an area that is on the Israeli side of the barrier;
- 68 units in the Tene settlement, located on the southern tip of the West Bank;
- 45 units in the Vered Yericho settlement, located just west of the Palestinian city of Jericho in the Jordan Valley;
- 27 units in the Karnei Shomron settlement, which is also expected to receive final approval for 82 units. Karnei Shomron is located in the northern West Bank, east of the Palestinian village of Qalqilya. Israel has openly declared its intention to continue expanding settlements in this area with the stated goal of bringing 1 million settlers to live in the area.;
- 18 units in the Alon Shvut settlement, which is also expected to receive final approval for 110 units. Alon Shvut is located just north of the Kfar Etzion settlement and between Bethlehem and Hebron;
- 10 units in the Tal Menashe settlement, located located on the tip of the northern West Bank, inside the “seam zone” between the 1967 Green Line and the Israel separation barrier, which was constructed along a route designed to keep as many settlements and as much adjacent land as possible on the Israeli side of the wall/fence.
- 7 units in the Hermesh settlement, located in the northern West Bank;
- 4 units in the Efrat settlement, located south of Bethlehem, inside a settlement block that cuts deep into the West Bank. Efrat’s location and the route of the barrier wall around it, have literally severed the route of Highway 60 south of Bethlehem, cutting off Bethlehem and Jerusalem from the southern West Bank. The economic, political, and social impacts of the closure of Highway 60 at the Efrat settlement (there is literally a wall built across the highway) have been severe for the Palestinian population.
Peace Now reports that the Planning Council will also consider advancing the following plans for Palestinian homes:
- 270 houses in the Bir al-Bash village, located south of Jenin in the northern West Bank;
- 270 houses in the Al-Ma’asara village, located south of Bethlehem;
- 233 houses in the the Almasqufa village, located near Tulkarem in the northern West Bank;
- 200 houses in the Dkeika village in the South Hebron Hills;
- 170 houses in the Khirbet Abdallah Younas village, located in the Jenin area;
- 160 houses in the Abba a-Sharqiya village, also located south of Jenin in the northern West Bank;
Israeli Supreme Court to Hold Hearing on Batan al-Hawa, Silwan Dispossession Cases Next Week; AG Declines Intervention
On October 25th, the Israeli Supreme Court is scheduled to hold an important hearing on the case of the Palestinian Duweik family which is under threat of being dispossessed of their longtime home in the Batan al-Hawa section of the Silwan neighborhood in East Jerusalem by the Ateret Cohanim settler organization.
In advance of that hearing – and after repeated extensions on a Court-ordered deadline – the Israeli Attorney General finally submitted his position on the case to the Court. The document submitted by the Attorney General was only 1 page, and simply stated that the case does not merit intervention either on the specific case of the Duweik family or regarding the wider legal principle at stake, which threatens an additional 85 families living under threat of eviction in Batan al-Hawa.
Ir Amim writes:
“Among the 85 families facing eviction, the Duweik family case is the first to reach the Supreme Court level, and its outcome will inevitably set a precedent, significantly impacting the rest of the cases in the neighborhood…As in the eviction cases in Sheikh Jarrah, the Attorney General and by extension, the government, was given a rare opportunity to take a moral stand by providing a legal opinion and policy position to help prevent the mass displacement of these families. Yet, at this point, the Attorney General’s response appears to imply that he has declined to intervene. Now, the decision concerning the fate of these families seems to lie solely in the hands of the Supreme Court. The rights of Palestinians to housing and shelter and the right to family and community life are fundamental and must be upheld. The same discriminatory legal system, which led to the confiscation of these families’ original homes in 1948, is now being exploited 73 years later to displace them for a second time from their current homes in which they have lived for decades. The Supreme Court has the power to make a principled and just decision to uphold the rights of these families to remain safely in their homes, free from the constant threat of being forcibly uprooted and driven from their homes and communities.”
Peace Now said in response to the AG’s decision to not intervene:
“The Attorney General’s response actually says that for the Israeli government, there is no problem to kick hundreds of residents out from their homes, on the basis of a discriminatory law, in favor of a settlement. The government was given an opportunity here to try to prevent moral injustice and political folly, but instead of taking a stand, it chose to remain on the sidelines, as if Silwan’s story, like that of Sheikh Jarrah, was a legal matter and not a political one.”
In July 2021, Peace Now assembled a coalition of Israeli lawyers to submit an amicus brief to the Court regarding the Duweik case. Peace Now summarizes:
“The brief addresses an approach that has emerged in international jurisprudence on human rights law which puts an emphasis on group vulnerability of occupants facing eviction and institutional, systemic discrimination against them. Where these are present, in certain circumstances, the occupants’ rights, stemming from the human right to housing and specifically, to live in their home and their family’s home – trump the right of the original owner or their substitute to regain possession of the property.
The brief reaches the conclusion that in the Duweik case, the occupants’ property rights and their right to housing supersede the right of the settlers acting on behalf of the pre-1948 original owners to receive possession of the property, based on the following:
1 – The fact that Palestinian residents of East Jerusalem are underprivileged, vulnerable and subjected to discrimination in every aspect of life, and particularly the fact that Israeli law on the restitution of property that changed hands due to wars, openly and deliberately discriminates against them;
2 – The fact that the family entered the property in good faith and/or in accordance with the law applicable at the time, and has developed a legitimate expectation to continue residing in it permanently and without interruption;
3 – The imbalance between the devastating harm the family would suffer and the minor damage the Benvenisti charitable endowment (represented by the settlers), which claims ownership of the property, would sustain, which clearly tips the scales in favor of the family.
In other words, according to the brief, even if the court finds the settlers do, in fact, have ownership, they are not necessarily entitled to remedy in the form of the families’ eviction from their homes, but rather to compensation from the state.”
Israel Begins Construction on New Settlement in Downtown Hebron
Peace Now reports that construction has begun on 31 new settlement units at the site of an old bus station previously repurposed as an IDF base, located in the heart of the Old City of Hebron on the infamous Shuhada street. This is a new settler enclave in the city and is, in effect, a new urban settlement, disconnected from already existing settlements in the city. It will be the first new settlement construction approved in downtown Hebron – where Palestinians already live under apartheid conditions – since 2002.
Peace Now said in a statement:
“The government is acting like an annexation government, not as a change government. Since the 1980s, no government has dared to build a new settlement in the heart of the largest Palestinian city in the West Bank, with the exception of one building built under the auspices of the second intifada in 2001. The Defense Minister has to stop construction, even if the plan was approved by the previous government. The settlement in Hebron is the ugly face of Israeli control of the territories. The moral and political price of having a settlement in Hebron is unbearable.”
As a reminder: in October 2017, the Israeli Civil Administration approved a building permit for the 31 units, on the condition that the Palestinian municipality of Hebron and others would have the opportunity to file objections to the plan. Soon after, two appeals were filed with the Defense Ministry: one by the Palestinian municipality of Hebron and one by the Israeli settlement watchdog Peace Now. The legal objections were based on the legally questionable process by which Israel made land in downtown Hebron available for settlement construction. Located in the Israeli-controlled H-2 area of Hebron (where 500 Israeli settlers live amongst 40,000 Palestinians), Israel seized the land in the 1980s from the Hebron Municipality, for military purposes. In 2007, the Civil Administration’s Legal Advisor issued an opinion stating that once Israel is done using the land for military purposes, it must be returned to the Hebron Municipality, which has protected tenancy rights to the land. Nonetheless, in 2015, the Israeli Civil Administration, with the consent of the Minister of Defense, quietly authorized the Housing Ministry to plan the area for Israeli settlement use, paving the way for that same ministry to subsequently present the plan for the 31 units.
In October 2018, with the legal challenges still pending, the Israeli Cabinet voted to expedite the planning of the new settlement and allocated approximately $6.1 million (NIS 22 million) for the project, which will require Israel to significantly renovate the bus station/military base in order to build the 31 new settlement housing units, as well as a kindergarten, and “public areas” for the new settler residents. Peace Now explains:
“The approval of the building permit in the heart of Hebron is an extraordinary move not only because it is a new settlement in Hebron for the first time since 2001, but because it indicates a significant change in Israeli legal interpretation of what is allowed and forbidden in occupied territory. The area in question was owned by Jews before 1948, and it was leased by the Jordanian government in protected tenancy to the Hebron municipality for the purpose of establishing the central bus station. Since 1967, the Israeli authorities managed the land and continued the lease to the Hebron municipality, until in the 1980s when the area was seized for military purposes, the bus station was closed and a military base was established there. A legal opinion of the Judea and Samaria Attorney General on the issue in 2007 emphatically stated that by law the municipality’s protected lease must not be revoked.”
Israel Advances “Silicon Wadi” Project in East Jerusalem
On October 13th, the Jerusalem Local Planning Committee met to initiate the planning process for the “Silicon Wadi” project, which was initiated by the Jerusalem Municipality and outlines plans to build a large industrial zone for hi-tech, commercial, and hospitality businesses in the heart of East Jerusalem’s Wadi Joz neighborhood. The project requires the demolition of some 200 Palestinian-owned businesses that currently operate in the area; dozens of demolition notices for which were issued in November 2020.
Ir Amim writes:
“Beyond the devastating impact of widespread demolitions of existing businesses and structures, the plan also raises concerns that the Israeli authorities will exploit the planning procedures to locate alleged Palestinian absentee properties and transfer lands into the hands of the State. It should also be noted that while Israel focuses on bolstering employment and economic activity in East Jerusalem, it simultaneously continues to suppress residential development in Palestinian neighborhoods. As with nearly all outline plans advanced in East Jerusalem in recent years, the Wadi Joz business park plan only allocates a marginal amount for residential use, which hardly meets the acute housing needs of the Palestinian population. Rather than undertaking measures to rectify the housing crisis, these plans only exacerbate the current situation and perpetuate the residential planning stranglehold, which ultimately serves to push Palestinians out of the city.”
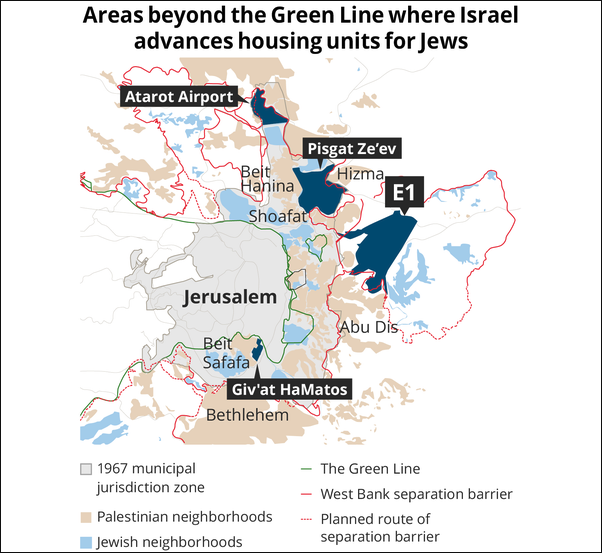
Recap: Israel Advances Settlement Plans Across Greater Jerusalem Area
Over the past two weeks, the government of Israel has advanced four highly controversial and politically consequential settlement plans in the Greater Jerusalem area:
- The Givat Hamatos Settlement: On October 13th, the Jerusalem Local Planning Committee approved the expropriation of lands designated for public use in the Givat Hamatos area for the construction of roads, public buildings and the development of open space for the planned new settlement/neighborhood. For more on the Givat Hamatos settlement plan, please see here.
- The E-1 Settlement: The Israel Civil Administration moved forward with advancing plans for the construction of the E-1 settlement, setting a date for a third hearing to discuss public objections to the plan (now set for November 8th). The first hearing was held on October 4th, but Palestinians were denied the ability to participate in that hearing (which was held virtually, making it inaccessible to the many Palestinians affected by the plan who do not have internet access). As a result, the Court scheduled this 3rd hearing (to allow the participation of Palestinians). The second hearing was held on October 18th; at that hearing three objections were presented (one by the Palestinian village of Anata, a second by the Palestinian village of Al-Azariya, and a third joint submission filed by Ir Amim and Peace Now). Ir Amim reports that there was no substantive discussion of these objections, with the Civil Administration panel offering no questions or comments on them. For more on the E-1 settlement plan, please see Terrestrial Jeruaslem’s excellent and thorough reporting.
- The Atarot Settlement: The Jerusalem District Planning Committee formally signaled that it will proceed with a hearing on the Atarot settlement plan – scheduled for December 6th – to build a huge new settlement on the site of the former Qalandiya airport (located at the northern tip of East Jerusalem). In its current form, the plan provides for up to 9,000 residential units for ultra-Orthodox Jews (assuming, conservatively, an average family size of 6, this means housing for 54,000 people), as well as synagogues, ritual baths (mikvehs), commercial properties, offices and work spaces, a hotel, and a water reservoir. If built, the Atarot settlement will effectively be a small Israeli city surrounded by Palestinian East Jerusalem neighborhoods on three sides and Ramallah to its north. Geopolitically, it will have a similar impact to E-1 in terms of dismembering the West Bank and cutting it off from Jerusalem. For more on the Atarot settlement plan, please see here.
- The Pisgat Ze’ev Settlement: The Israeli government advanced plans for 470 new settlement units in Pisgat Ze’ev, the largest settlement located in East Jerusalem.
Recap: Court Pushes for Palestinians to “Compromise” with Settlers in Sheikh Jarrah
The Israeli Supreme Court has set November 2nd as the deadline for Palestinian families living at risk of forced displacement in Shiekh Jarrah to decide wether or not to accept a Court-authored deal which would help them – at least temporarily – avoid eviction from their homes, in part by requiring them to recognize settler ownership over the properties.
Under the terms of the Court’s deal, which it is pressuring both parties to accept, the following would take place:
- The settler group Nahalat Shimon will be recognized as the owners of the site.
- The Palestinians will be recognized as protected tenants and be required to pay an nominal annual rental fee to the attorney of the settlers (in effect recognizing the settlers as the owners) but
- The Palestinians will be able to continue pursuing legal challenges to the underlying ownership of the land
- The Palestinians are permitted to renovate the properties without interference
- Settlers will be able to instigate eviction proceedings against Palestinians if they are in violation of the Court’s compromise agreement or in violation of Israel’s tenancy laws.
Terrestrial Jerusalem writes:
“The most problematic element of the settlement relates to the settlers’ ability to institute evictions even if the residents are not in violation of the agreement or of the tenancy laws. The settlers will be entitled to institute such proceedings in the event that the ownership rights are conclusively awarded to them, or after 15 years, the earlier of the two. This can be done if the settlers either wish to personally use the property or to demolish and rebuild. Under these circumstances, the settlers will need to offer the residents alternative equivalent quarters. Palestinian residents might hope settlers reject the deal to avoid having to make an ‘excruciatingly painful decision.’”
According to Terrestrial Jerusalem, the Court has signaled that further negotiations are acceptable, but that if either party rejects the agreement a decision on the eviction cases will be handed down swiftly.
New Report: State-Backed Settler “Tourism” Projects in East Jerusalem
In a new report entitled, “The Valley of Hinnom: Trees and Flowerbeds in the Political Struggle over East Jerusalem,” the Israeli NGO Emek Shaveh surveys the multitude of recent “tourism” projects jointly undertaken by the Elad settler organization and the Israeli government in the Ben Hinnom Valley — a strategic area between East and West Jerusalem (stretching past the 1967 Green Line), and located within the area designated by Israel as the Jerusalem “Walls National Park”.
Emek Shaveh writes:
“The nature of the tourism-settlement activity in the Valley of Hinnom conducted jointly by Elad and government authorities is familiar to us from the City of David/Silwan. The series of joint ventures such as the café, the Center for Ancient Agriculture and the cable car in effect hand over large expanses of land to the settlers of the Elad Foundation under the guise of tourism. Although unlike Silwan, the valley is sparsely populated, the activity there must be viewed as an integral part of the struggle for the Old City Basin of Jerusalem and as a means to clear this highly strategic area from the presence of Palestinians.”
In conclusion, we wish to emphasize the following points:
1 – Development in East Jerusalem is almost always driven by political objectives. Recent developments in the Valley of Hinnom are part of the grand plan to change the character and the landscape of the Old City Basin and ought to be considered an integral component of the settlement enterprise in the Palestinian neighborhoods surrounding the Old City.
2 – Halting the destructive development schemes in the areas surrounding the Old City is vital in order to preserve Jerusalem as a multicultural historic city and is indirectly essential for safeguarding the status quo at the holy places.
3 – The Palestinian protests against the expansion of the settlers’ grip over the open spaces such as the Hinnom Valley is part of the struggle by the residents of Silwan and the surrounding neighborhoods to preserve the character of their neighborhoods. In our view, one ought to view the various activities by the settlers and the authorities in the Historic Basin such as the expulsion of residents from their homes, taking over land and the shaping of a historic narrative as part of the same general bid to cement their control over the Historic Basin.”
Bonus Reads
- “[PODCAST] The Occupation & the Biden Administration” (FMEP ft. Danny Seidemann and Yehuda Shaul with Lara Friedman and Khaled Elgindy)
- “How offshore accounts turned the British Virgin Islands into an east Jerusalem landlord” (JTA)
- “Beita residents reach lands for first time since settler takeover” (Al Jazeera)
- “After Years of Neighborly Relations, Settlers Try to Foil Recognition of Palestinian Hamlet” (Haaretz)
- “Palestinian protests turn deadly as Israel considers the future of a new settlement” (NPR)
- “These Palestinian Families Face Eviction From Their East Jerusalem Homes” (Haaretz)
- “When Settler Becomes Native” (Jewish Currents)